1. Foreman OpenSCAP manual
This plugin enables Foreman to receive automated vulnerability assessment and security compliance audits from Foreman hosts. You can upload SCAP compliance contents, create compliance policies out of them and assign the policies to hosts or hostgroups. foreman_openscap plugin provides three default SCAP contents, so you could start testing security compliance on RHEL6/7 and Fedora.
OpenSCAP reports (aka ARF reports) will help you find vulnerabilities on your hosts and also suggest remediation plan to fix those vulnerabilities.

Foreman OpenSCAP plugin is made of several components:
- foreman_openscap - Foreman plugin which creates and persists SCAP content, compliance policy and ARF report objects.
- smart_proxy_openscap - Smart-Proxy plugin which validates SCAP content from Foreman, distributes SCAP content to clients and posts ARF reports from client hosts to Foreman
- foreman_scap_client - A client script which runs OpenSCAP scan and uploads the scan report to the Smart-Proxy
- puppet-foreman_scap_client - A puppet module which configures foreman_scap_client
- ansible-foreman_scap_client - Ansible role which configures foreman_scap_client, an alternative to puppet-foreman_scap_client
1.1 OpenSCAP basic concepts
There are four basic concepts (entities) in OpenSCAP plug-in: SCAP Contents, Compliance Policies, ARF Reports and Tailoring Files.
SCAP Content represents SCAP DataStream XML file as defined by SCAP 1.2 standard. DataStream file contains implementation of compliance, configuration or security baselines. Users are advised to acquire examplary baseline by installing scap-security-guide package. DataStream file usualy contains multiple XCCDF Profiles. Each for different security target. The content of DataStream file can be inspected by oscap tool from openscap-scanner package. (XCCDF = Extensible Configuration Checklist Description Format, XCCDF profile = A checklist which audit specific security target)
Tailoring File is a XML file very much like SCAP Content. It represents a customization of compliance defined in a SCAP Content XML file. Additional details and instructions how to create such a file are available in the official openscap documentation.
Compliance Policy is high level concept of a baseline applied to the infrastructure. Compliance policy is defined by user on web interface. Users may assign following information to the policy:
- Deployment Options - how the client will be deployed. The options are Ansible (provided you have foreman_ansible plugin), Puppet or manual. It is recommended to use Puppet or Ansible for client deployment as they provide a convenient way of applying changes. See section 2.3 for details on policy deployment options.
- SCAP Content
- XCCDF Profile from particular SCAP Content
- Tailoring File
- XCCDF Profile from a Tailoring File
- Hostgroups that should comply with the policy
- Schedule - the period in which the audit shall occur
ARF Report is XML output of single scan occurrence per single host. Asset Reporting File format is defined by SCAP 1.2 standard. Foreman plug-in stores the ARF Reports in database for later inspections.
1.2 Release notes
Compatibility matrix
| Foreman version | Plugin version | Proxy version | Client version |
|---|---|---|---|
| = 1.7 | 0.3.4 | 0.3.1 | 0.1.1 |
| >= 1.8 | 0.4.1 | 0.4.0 | 0.1.1 |
| >= 1.11 | 0.5.0 | 0.5.0 | 0.1.2 |
| >= 1.13 | 0.6.0 | 0.6.0 | 0.2.0 |
| >= 1.15 | 0.7.0 | 0.6.0 | 0.3.0 |
| >= 1.16 | 0.8.0 | 0.6.0 | 0.3.0 |
| >= 1.17 | 0.9.0 | >=0.6.0 | 0.3.0 |
2. Installation
There are a few components to install:
- Foreman OpenSCAP (foreman_openscap)
- Smart Proxy OpenSCAP (smart_proxy_openscap)
- puppet-foreman_scap_client or ansible-foreman_scap_client
2.1 Installing foreman_openscap
The easiest and recommended way is using foreman-installer. It’s as easy as running this command
> foreman-installer --enable-foreman-plugin-openscap
If you prefer the manual way, you can install it from package like this:
> yum install tfm-rubygem-foreman_openscap
> foreman-rake db:migrate
> foreman-rake db:seed
> service httpd reload
Please refer to the Foreman plugin manual for more information about installing Foreman plugins.
2.2 Installing smart_proxy_openscap
The easiest and recommended way is using foreman-installer. It’s as easy as running this command
> foreman-installer --enable-foreman-proxy-plugin-openscap
If you run Smart-Proxy with Foreman on the same host you can combine it with –enable-foreman-plugin-openscap option.
If you prefer the manual way, install this package on the Smart-Proxy server:
> yum install rubygem-smart_proxy_openscap
Edit /etc/foreman-proxy/settings.d/openscap.yml with the appropriate settings
---
:enabled: true
# Log file for the forwarding script.
:openscap_send_log_file: /var/log/foreman-proxy/openscap-send.log
# Directory where OpenSCAP audits are stored
# before they are forwarded to Foreman
:spooldir: /var/spool/foreman-proxy/openscap
# Directory where OpenSCAP content XML are stored
# So we will not request the XML from Foreman each time
:contentdir: /var/lib/openscap/content
# Directory where OpenSCAP report XML are stored
# So Foreman can request arf xml reports
:reportsdir: /usr/share/foreman-proxy/openscap/reports
# Directory where OpenSCAP report XML are stored
# In case sending to Foreman succeeded, yet failed to save to reportsdir
:failed_dir: /usr/share/foreman-proxy/openscap/failed
# Directory where corrupted OpenSCAP report XML are stored
# When proxy cannot parse the report sent by client
:corrupted_dir: /var/lib/foreman-proxy/openscap/corrupted
# Timeout for sending OpenSCAP reports to Foreman server, in seconds
:timeout: 60
2.3 Policy deployment options
Workflow with Puppet and Ansible is similar. In the first step, you install appropriate package and import module or role which takes care of the client deployment. Foreman overrides parameters/variables for port, server and policies behind the scenes to make sure appropriate configuration is available to the client. When configuration is applied to host, foreman_scap_client is installed, client config is written to /etc/foreman_scap_client/config.yaml and a cron that will upload reports based on configuration of each policy is created.
It is important to make sure foreman_scap_client package is available to your client system. Foreman plugins repo can be optionally enabled using the appropriate parameters/variables. The repo is disabled by default as users may prefer to use their own mirror.
2.3.1 Puppet
Recommended way is to install the packaged version from our repositories:
yum -y install puppet-foreman_scap_client
Then import the module into Foreman.
The Puppet module is available on Puppet Forge, please be aware that the latest version in Forge might not be compatible with your version of Foreman.
puppet module install theforeman-foreman_scap_client
Detailed parameter description can be found in the module’s documentation.
2.3.2 Ansible
Please read section about client authentication if running Foreman without Katello. Recommended way is to install the packaged version from our repositories:
yum -y install ansible-foreman_scap_client
Then import the role into Foreman.
Ansible role is available on Ansible Galaxy, please be aware that the latest version in Galaxy might not be compatible with your version of Foreman.
ansible-galaxy -p /etc/ansible/roles install theforeman.foreman_scap_client
Detailed variable description can be found in the role’s documentation.
2.3.3 Manual
Manual policy deployment does not require to install anything, but leaves configuration to user. See section 4.6.2 for details.
3. Upgrading from 0.4.x
As with any Foreman plugin, the recommended upgrade path is done via yum upgrade. This will ensure that all of the packages are with the right version, dependencies
and data migrations.
Note: ARF reports are not automatically migrated and need a manual step
3.1 Migrating ARF reports from 0.4.x
ARF reports in 0.5.x and Foreman > 1.11 are now part of Foreman’s reports (Reports STI), and the physical ARF report XML is now saved at the Smart-Proxy.
This requires a special migration, which needs both Foreman and Smart-Proxy up and running, with latest respective OpenSCAP plugins installed.
Since we cannot assure this during upgrade, migration of ARF reports has moved to a rake task which should be performed after upgrading.
To upgrade ARF reports from 0.4.x to 0.5.x:
- Upgrade foreman_openscap to version 0.5.x
- Upgrade smart_proxy_openscap to version 0.5.x
- Run
foreman-rake db:migrateto ensure all other data has been migrated - Restart Foreman and Smart-Proxy
- Run
foreman-rake foreman_openscap:migrate[<proxy_id>](Where<proxy_id>is the id of the Smart-Proxy with OpenSCAP feature).
Notes: to find out your Smart-Proxy id you can either run hammer proxy list or pick the Smart-Proxy’s id from the url in web UI. please note it should be inside the square brackets
Process: During the ARF reports migration, the old ARF reports are fetched from the Foreman database, sent to the Smart-Proxy for re-processing and saving and are sent back to the Foreman in their new format - while keeping their original data.
Once the old ARF report has successfully migrated, it is deleted from the old table.
4. Usage
This chapter covers features that you can use in terms of Foreman and OpenSCAP integration. Everything described below assumes you’ve sucessfully completed the installation steps described in previous sections.
Please note: smart_proxy_openscap is required for the normal operation of foreman_openscap
You would usually start with uploading SCAP contents, then create policies of those SCAP contents and assign the policy to hosts or hostgroups.
4.1 Creating SCAP content
4.1.1 Creating default SCAP content
When installing foreman_openscap from RPM, we also add default SCAP content provided by scap-security-guide.
In previous versions, the default SCAP content was added via seed task.
In version >= 0.5.x, we are processing all of OpenSCAP content and reports in the Proxy.
And we are unsure if during installation the smart_proxy_openscap plugin is installed and enabled, so we can not seed the default SCAP content. Instead of auto-generating default SCAP content when installing foreman_openscap, you can now accomplish that with a rake task.
Creating default SCAP content
- Install smart_proxy_openscap on one (or more) of your proxies
- Refresh features of that proxy (so it will register with OpenSCAP feature on the Foreman)
- from terminal run
foreman-rake foreman_openscap:bulk_upload:default
This will search for scap-security-guide SCAP contents and create SCAP content on the Foreman.
4.1.2 Uploading SCAP content
Besides the default SCAP content, you can also upload your own SCAP content.
Access SCAP contents - Hosts -> Compliance -> SCAP Contents
Create SCAP Content - You can upload any valid OpenSCAP DataStream file
(After upload, SCAP content is validated at the Smart-Proxy and SCAP profiles are extracted)

4.2 Creating policy wizard
- Deployment options - choose how foreman_scap_client will be deployed. Make sure you have theforeman-foreman_scap_client module for Puppet or theforeman.foreman_scap_client role for Ansible imported first
- Name your policy
- Choose which SCAP content & SCAP profile to apply
- Choose schedule when to run this policy
- Select which locations / organizations this policy belongs to, if enabled
- Choose which hostgroups you wish apply this policy

4.3 Assigning policy to host
You can assign a policy in two ways:
- By assigning a policy to hostgroup(s) when creating / editing a policy. All hosts which belong to that hostgroup will automatically be assigned to the policy.
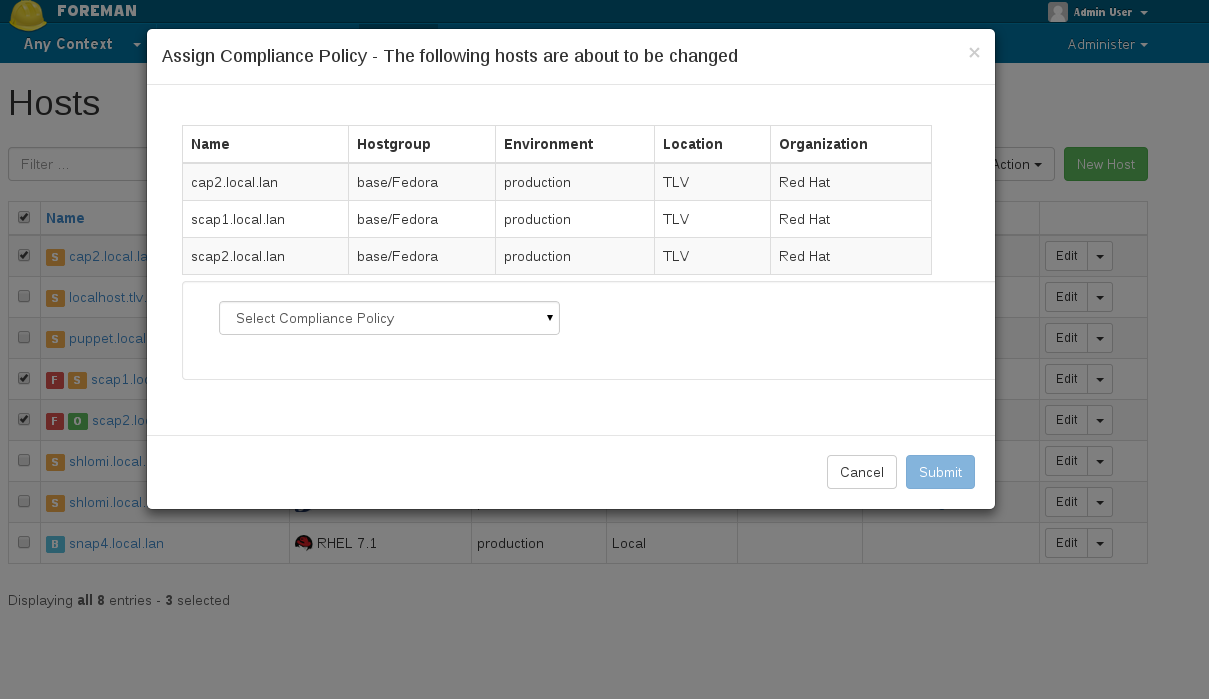
- By assigning a policy to host(s) via hosts index: In the hosts index, choose the hosts you wish to assign a policy. Click on ‘Select Action’ and choose: “Assign Compliance Policy” and choose which policy to assign to the selected hosts.
4.4 ARF Reports
You can access the generated reports via Hosts -> Compliance -> Reports
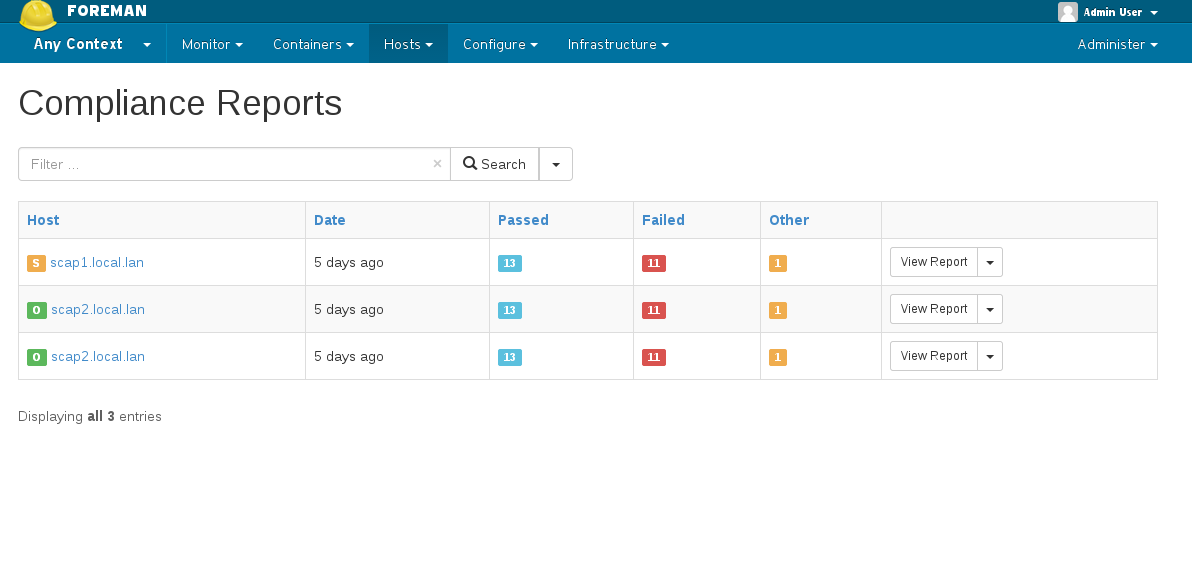
Report page gives information about individual rules that were checked during scan. Here you can download the actual report generated by OpenSCAP in HTML or as XML in bzip archive.
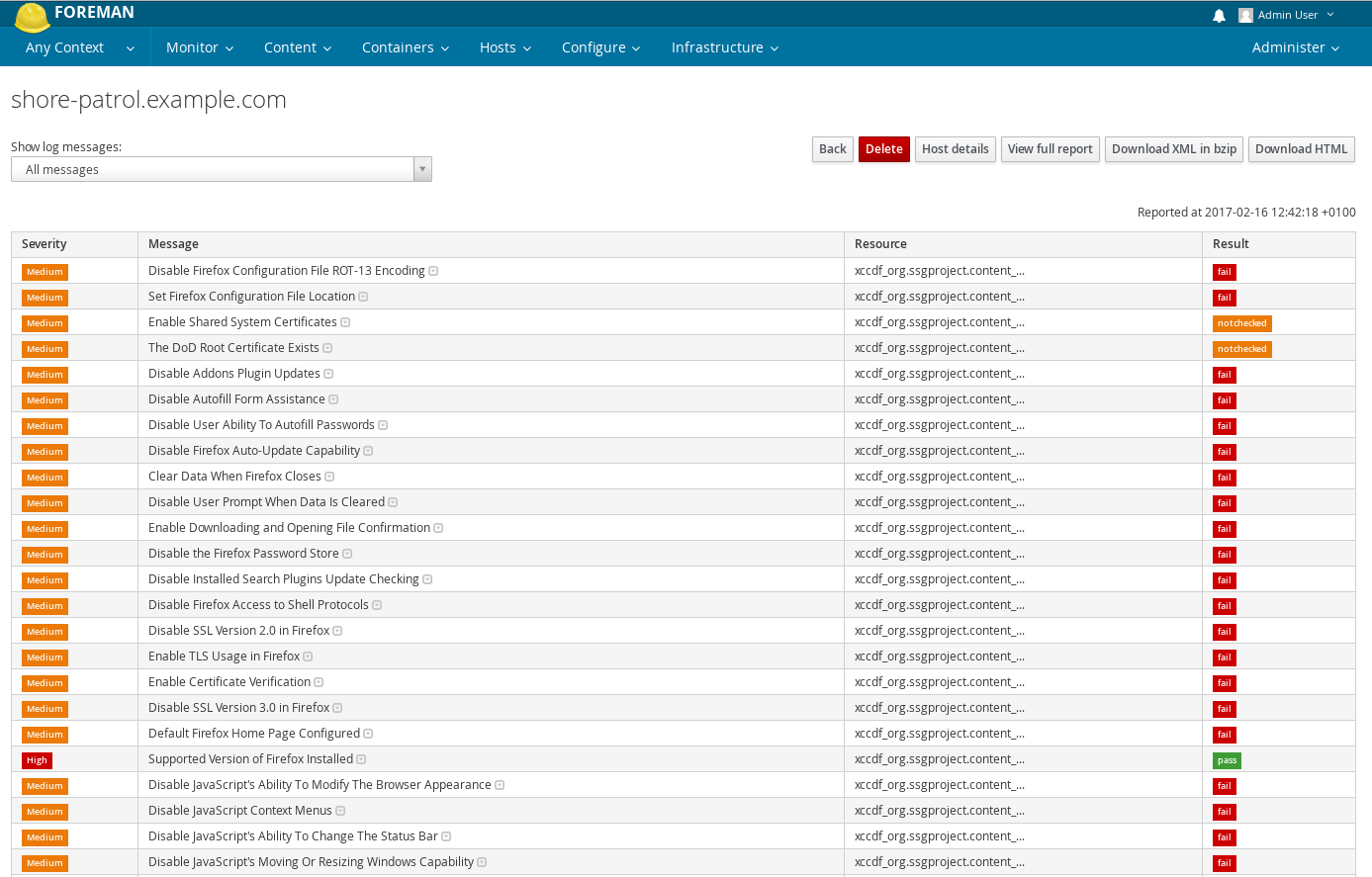
Clicking on “View full report” at the top of the page will lead you to the actual security audit report generated by OpenSCAP, with detailed information on the host’s security check and suggested remediation.

4.5 Tailoring files ( foreman_openscap >= 0.6.5 )
Using a Tailoring File effectively allows you to modify a policy. You can assign a Tailoring File to a Policy when creating / updating a policy. Because Tailoring File may contain multiple profiles, you have to select your modified profile as well.
4.5.1 Creating a Tailoring file
You can create a new Tailoring file with SCAP Workbench
4.5.2 Uploading a Tailoring file
Access Tailoring files - Hosts -> Compliance -> Tailoring files
Create Tailoring - Upload your Tailoring file xml
4.5.3 Assigning a Tailoring file to a Policy
Go to Hosts -> Compliance -> Policies
Select a Policy to edit
Go to ‘SCAP Content’ tab
Select a Tailoring file from a dropdown and then a profile that comes with it

4.6 Setting up hosts for scans
There are 3 important things that your host needs to have so that it can be scanned properly:
-
Policy - you can assign it directly or via hostgroup. See section 4.3 for details.
-
foreman_scap_client Puppet module or Ansible role - it will take care of configuring the host with foreman_scap_client. Note that while puppet runs are scheduled periodically, you need to apply Ansible roles to propagate changes as Ansible does not run automatically. foreman_scap_client is a ruby script that runs the openscap scanner with configured options. You can assign module/role to the host such as you would any other module. See the section for Puppet Classes or Ansible roles for details.
-
Openscap proxy - All the communication between Foreman and hosts goes through the proxy with Openscap feature (provided by smart_proxy_openscap). You need to choose which one should be used for each host. You can do that under Hosts -> All hosts, Edit.
4.6.1 Authenticating clients
This section is relevant for Ansible and Foreman installations without Katello or manual policy deployments. Otherwise no action is required and this section can be skipped.
4.6.1.1 Using Ansible when Foreman installation does not include Katello
foreman_openscap does not create its own way to authenticate clients, but relies on already established certificate infrastructure when foreman_scap_client uploads reports to proxy. The proxy is either configured to use consumer certificates when your Foreman instance includes Katello, or Puppet certs when running vanilla Foreman. With Katello, consumer certificates are created for subscribed hosts and foreman_scap_client is able to use them to authenticate. Without Katello, Puppet certs are by default accepted by proxy when authenticating clients, which poses a problem when Ansible is used on hosts to deploy foreman_scap_client instead of Puppet - there are no certificates which client can use.
It is still possible to use Puppet CA generated certs to authenticate these clients. You need to generate the certificates yourself on your Puppet CA server:
puppet cert --generate ${client-fqdn}
Copy the following certificates to your client:
- /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem
- /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/${client-fqdn}.pem
- /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/${client-fqdn}.pem
Configure appropriate Ansible variables of theforeman.foreman_scap_client with certificate paths on the client, for example:
foreman_scap_client_ca_cert_path: /etc/foreman_scap_client/ssl/certs/ca.pem
foreman_scap_client_host_cert_path: /etc/foreman_scap_client/ssl/certs/${client-fqdn}.pem
foreman_scap_client_host_private_key_path: /etc/foreman_scap_client/ssl/private_keys/${client-fqdn}.pem
Apply theforeman.foreman_scap_client role on your host, which will configure the cert paths for client and it will be able to authenticate.
4.6.2.2 Using manual policy deployment option
If user decided to use manual option and your Foreman installation does not include Katello, then steps for generating and copying certificates from the previous section applies. It is necessary to add paths to certificates to /etc/foreman_scap_client/config.yaml.
If your installation includes Katello, you need the consumer certificates:
- /etc/rhsm/ca/katello-server-ca.pem
- /etc/pki/consumer/cert.pem
- /etc/pki/consumer/key.pem
4.6.2 Manual policy deployments
If a user chooses Manual as a policy deployment, Foreman will not care about client configuration and will leave it entirely up to user to configure clients. Multiple manual steps will be required to configure clients to send reports (which can be automated by using Ansible or Puppet).
1) Install foreman_scap_client package on the client.
2) Create client config in /etc/foreman_scap_client/config.yaml and populate it with appropriate values. See example config in section 6.3. The most convenient way to get the attributes for policies is to add a host parameter with <%= @host.policies_enc %> value to your client and then get the JSON value it generates from ENC.
3) Make sure client has access to certificates to authenticate (See previous section for details).
Please note that any changes made in Foreman do not propagate to your clients as it is handled by Puppet module/Ansible role. When you add/remove policies to your hosts or modify existing policies in any way, you need to update the config on client manually.
4.7 Running a scan from UI ( foreman_openscap >= 0.6.5 )
In version 0.6.5 and higher, you can initiate scans from UI. Simply go to hosts page and select “Run OpenSCAP scan” from the dropdown menu. This will initiate a scan for all policies that are assigned to the host. foreman_remote_execution plugin of version 1.3.0 or higher needs to be installed for this feature to be enabled.

4.8 Searching
If you scan your hosts often, you may find yourself in a situation where lots of reports are uploaded to your Foreman instance and the quantity makes it more difficult to quickly find the information you need. There are several search queries that aim to assist you with this task. All you need to do is type the appropriate scoped search query into the search bar.
4.8.1 Searching for Policies
You can search for policies by name:
name = my_policy
4.8.2 Searching for Scap Contents and Tailoring Files
You can search Scap Content on title and Tailoring file on name (same as policies). You can search both on original file name:
filename = ssg-jre-ds.xml
4.8.3 Searching for Reports
You can search reports by policy name:
policy = my-policy
# or
compliance_policy = my-policy
You can get the last reports for host or policy:
last_for = host
last_for = policy
You can search for reports that comply, do not comply or are inconclusive for a specific policy:
comply_with = my-policy
not_comply_with = my-policy
inconclusive_with = my-policy
You can get reports based on Openscap proxy that parsed and uploaded them:
openscap_proxy = my-openscap-proxy-name
You can view reports with a certain xccdf rule:
xccdf_rule_name = xccdf_org.ssgproject.content_rule_firefox_preferences-auto-download_actions
You can search for reports where a certain rule passed, failed or othered:
xccdf_rule_failed = xccdf_org.ssgproject.content_rule_firefox_preferences-auto-download_actions
xccdf_rule_passed = xccdf_org.ssgproject.content_rule_firefox_preferences-auto-download_actions
xccdf_rule_othered = xccdf_org.ssgproject.content_rule_firefox_preferences-auto-download_actions
You can search the reports based on compliance status:
compliance_passed
compliance_failed
compliance_othered
4.8.4 Searching for Hosts
You can search hosts by policy name or id. You can also find hosts that have policy assigned but no reports for that policy:
compliance_report_missing_for = my-policy
You can search hosts by compliance status:
compliance_status = compliant
compliance_status = incompliant
compliance_status = inconclusive
You can view hosts based on a current result of a rule:
fails_xccdf_rule = xccdf_org.ssgproject.content_rule_firefox_preferences-auto-download_actions
passes_xccdf_rule = xccdf_org.ssgproject.content_rule_firefox_preferences-auto-download_actions
others_xccdf_rule = xccdf_org.ssgproject.content_rule_firefox_preferences-auto-download_actions
5. Advanced topics
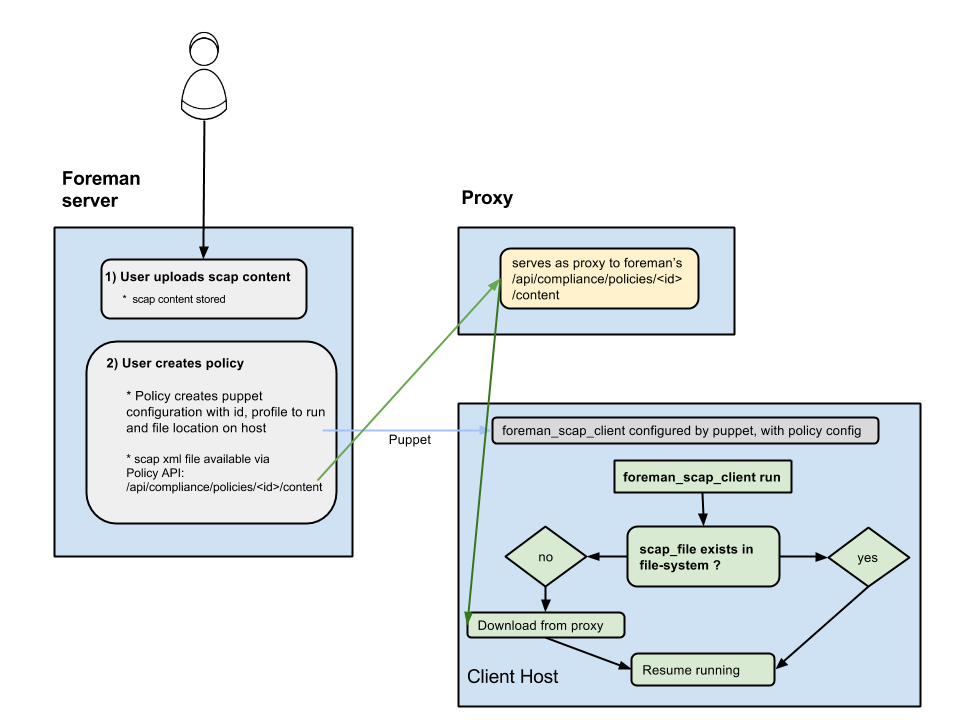
5.1 Distributing SCAP content with Foreman & Proxy
- Exposes a url on Foreman for downloading the scap file for the policy (
/api/compliance/policies/\<policy_id\>/content) - OpenSCAP plugin on Proxy serves as a (dumb) proxy to the above url (meaning, calling something like:
https://\<proxy_url\>/compliance/policies/\<policy_id\>/content/\<digest\>will fetch the xml fromhttps://\<foreman_url\>/api/compliance/policies/\<policy_id\>/content) - When foreman_scap_client starts running, it checks if the file configured by puppet exists. If it exists, it will resume operation. If it doesn’t exist, it will download the file from the Proxy and resume its operation.
5.2 Validating SCAP content on the proxy
- When uploading an SCAP content to Foreman it sends the file for validation at the Smart-Proxy:
- The Smart-Proxy validates that the SCAP xml file is a valid OpenSCAP file, and returns the errors if not.
- Once the SCAP content is validated, the Smart-Proxy is extracting the SCAP profiles for later use when creating a policy.
5.3 Arf Report retrieval process
- The client host is running oscap test and uploads ARF report to the Smart-Proxy as an XML file.
- The Smart-Proxy parses the XML and generates a JSON report.
- Once the JSON report has been successfully posted to the Foreman, the XML file is saved on the Smart-Proxy’s filesystem for later use from the Foreman
- (If the post to the Foreman fails the file is saved for later retry)
- On the Foreman side:
- The ARF report receives the JSON formatter report from the proxy and generates the report, its logs and messages.
- The complete report can be downloaded from the Smart-Proxy as a compressed XML, or viewed in OpenSCAP style HTML.

6. Help
There are several contact channels where you can reach us if you have any problems or questions. While you are waiting for our response, the following debugging steps might help you.
6.1 Running with Katello
When running with Katello, make sure your host is registered as Content Host because consumer certificates are used for client authentication instead of Puppet certs. Having unsubscribed hosts with Katello results in SSL cert verification error when foreman_scap_client tries to upload a report.
6.2 Scans based on cronlines
Scanning and report generation are based on cron. You can inspect all the cron lines in /etc/cron.d/foreman_scap_client_cron. This file is managed by Puppet/Ansible and any manual changes will be automatically overwritten.
6.3 Config for client
Config file for foreman_scap_client is located at /etc/foreman_scap_client/config.yaml. It should look something like this:
# DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE MANUALLY
# IT IS MANAGED BY PUPPET
# Foreman proxy to which reports should be uploaded
:server: 'somewhere.example.com'
:port: 8443
## SSL specific options ##
# Client CA file.
# It could be Puppet CA certificate (e.g., '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem')
# Or (recommended for client reporting to Katello) subscription manager CA file, (e.g., '/etc/rhsm/ca/katello-server-ca.pem')
:ca_file: '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ca.pem'
# Client host certificate.
# It could be Puppet agent host certificate (e.g., '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/certs/myhost.example.com.pem')
# Or (recommended for client reporting to Katello) consumer certificate (e.g., '/etc/pki/consumer/cert.pem')
:host_certificate: '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/certs/ada-bivens.example.com.pem'
# Client private key
# It could be Puppet agent private key (e.g., '/var/lib/puppet/ssl/private_keys/myhost.example.com.pem')
# Or (recommended for client reporting to Katello) consumer private key (e.g., '/etc/pki/consumer/key.pem')
:host_private_key: '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/private_keys/ada-bivens.example.com.pem'
# policy (key is id as in Foreman)
1:
:profile: 'xccdf_org.ssgproject.content_profile_stig-java-upstream'
:content_path: '/var/lib/openscap/content/fe93f99c14251cc76e92b9da71c351c8ba45fbd3639a2cd55911ef6f7db1b650.xml'
# Download path
# A path to download SCAP content from proxy
:download_path: '/compliance/policies/1/content/fe93f99c14251cc76e92b9da71c351c8ba45fbd3639a2cd55911ef6f7db1b650'
:tailoring_path: ''
:tailoring_download_path: ''
There will be an entry for each policy that is assigned to your host. The policy entry starts by number followed by colon. Policy attributes are indented by 2 spaces. This file is also managed by Puppet and any manual changes will be rewritten on next Puppet agent run.
6.3 Running scans manually
You can try running foreman_scap_client manually by executing
foreman_scap_client $policy_id
from your command line, where $policy_id is a policy id from config file (1 in case of example config file above)
6.4 Information in logs
If running scan manually succeeds and there are no errors, try switching logging to DEBUG on proxy with openscap feature that your host uploads reports to and restart the proxy. Then use
tail -f /var/log/foreman-proxy/proxy.log
and run foreman_scap_client manually again. Tailing the proxy logs will give you more insight into what is going on when report is uploaded by a client. Tailing /var/log/foreman/production.log on your Foreman server might be usefull as well.
6.5 Slow queries due to many message records in database ( foreman_openscap >= 0.7.2 )
Fix #19527 introduced a performance improvements to some of report-related queries and also added a rake task that performs a cleanup of database by removing duplicated report messages. You can execute it by running:
foreman-rake foreman_openscap:clean_messages
Please note that the task has to go through all your reports and it may take a significant amount of time to fininsh. We recommend expiring the reports that are no longer needed before running the task. This task does not need to be run more than once as the patch prevents the duplicates from being created.
6.6 Cleaning up reports without OpenSCAP proxy ( foreman_openscap >= 0.8.4 )
Fix #21091 added a rake task that deletes all reports that do not have and associated proxy with OpenSCAP feature. Apparently, some workflows may lead to proxy not being associated which causes problems when users try to delete hosts with such reports. You can execute it by running:
foreman-rake foreman_openscap:clean_reports_without_proxy
7. Getting involved
Follow the same process as Foreman for contributing.
8. Links
- foreman_openscap plugin https://github.com/theforeman/foreman_openscap
- smart_proxy_openscap plugin https://github.com/theforeman/smart_proxy_openscap
- foreman_scap_client https://github.com/theforeman/foreman_scap_client
- puppet-foreman_scap_client https://github.com/theforeman/puppet-foreman_scap_client
- ansible-foreman_scap_client https://github.com/theforeman/ansible-foreman_scap_client
- Issue tracker http://projects.theforeman.org/projects/foreman_openscap/issues