Katello 3.18 Documentation
Docker Management
Katello can be used to manage and deploy Docker content. Katello can retreive Docker content from a variety of sources such as Docker hub, private Docker registries, the Red Hat CDN, and so forth. Docker content can then be published and promoted via Content Views and then pulled or proivisioned to a server running Docker.
What is Docker?
Docker is a tool used to manage Linux containers. To read more about Docker, check out the official Docker site. Docker repositories, which contain images and tags, can be retrieved, stored, managed, and deployed from Katello.
How to sync a Docker repository
The easiest way to get Docker content into Katello is to sync it in. You can either sync Docker content from the Red Hat CDN (if you have subscriptions for the content) or from a registry such as Docker Hub.
Red Hat Docker Images
Content can be synced into Katello using a Red Hat manifest in much the same way as yum content. See our guide on how to manage Red Hat content for more information.
Docker Hub/Docker Registry
To sync content from a Docker registry such as Docker Hub (which is the official Docker-run registry), simply start by creating a new Repository.
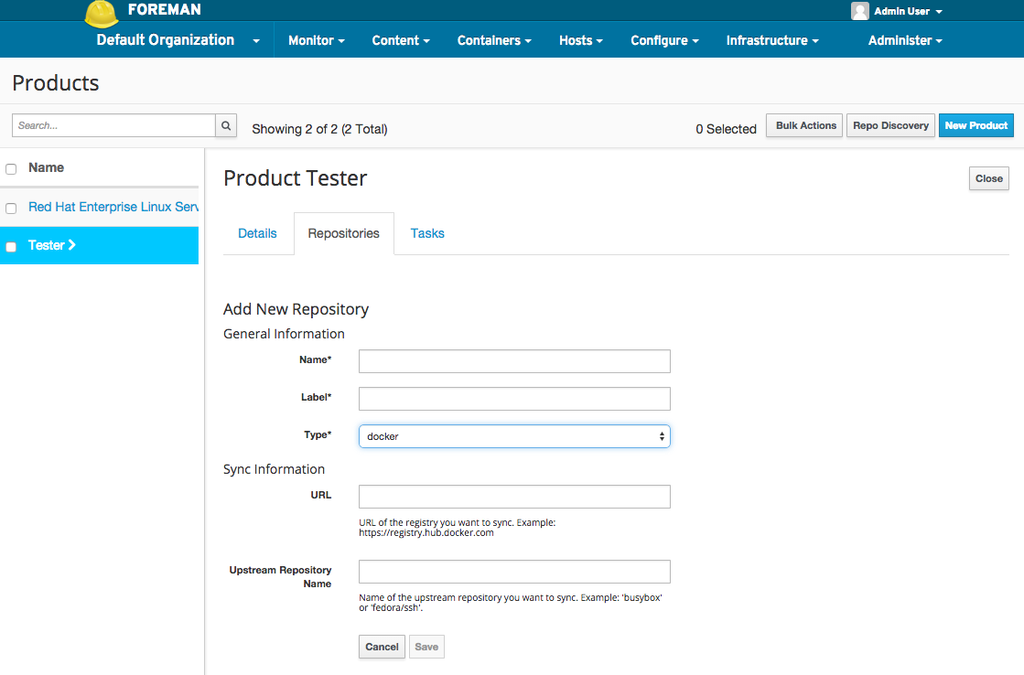
On the new Repository screen, select “Docker” as the content type. Once you do that, you’ll be given two options: upstream name and URL. The URL will be the registry URL; for Docker Hub, this would be https://registry-1.docker.io/.
For the upstream name, you want to use the fully qualified upstream name which also includes any namespace such as the username. This can be just “busybox” if the Repository is an official Docker Hub Repository or it can be something like “fedora/ssh” where “fedora” is the username/namespace.
Then click save and then sync the Repository as you normally would. Katello will fetch all the images and tags contained within that Repository.
How to Upload Docker Images
In versions of Katello prior to 3.0, Docker images could be uploaded directly via either the UI or CLI. However, Katello 3.0 only supports the Docker Registry v2 format, which is significantly different than the Docker Registry v1 format. The docker save command outputs a Docker image in v1 format, which cannot be uploaded directly to a v2 repository.
As a workaround, you can create a local Docker registry like so:
docker run -p 5030:5000 --name registry registry:2
Note the :2 above, which specifies a v2 registry. Push your changes to your newly created local registry then follow the instructions in the section above to sync this registry to Katello. This will ensure that your Docker content stays in Docker’s v2 registry format.
How to Publish and Promote Docker Content
Docker content can be published and promoted via Content Views much like yum or puppet content.
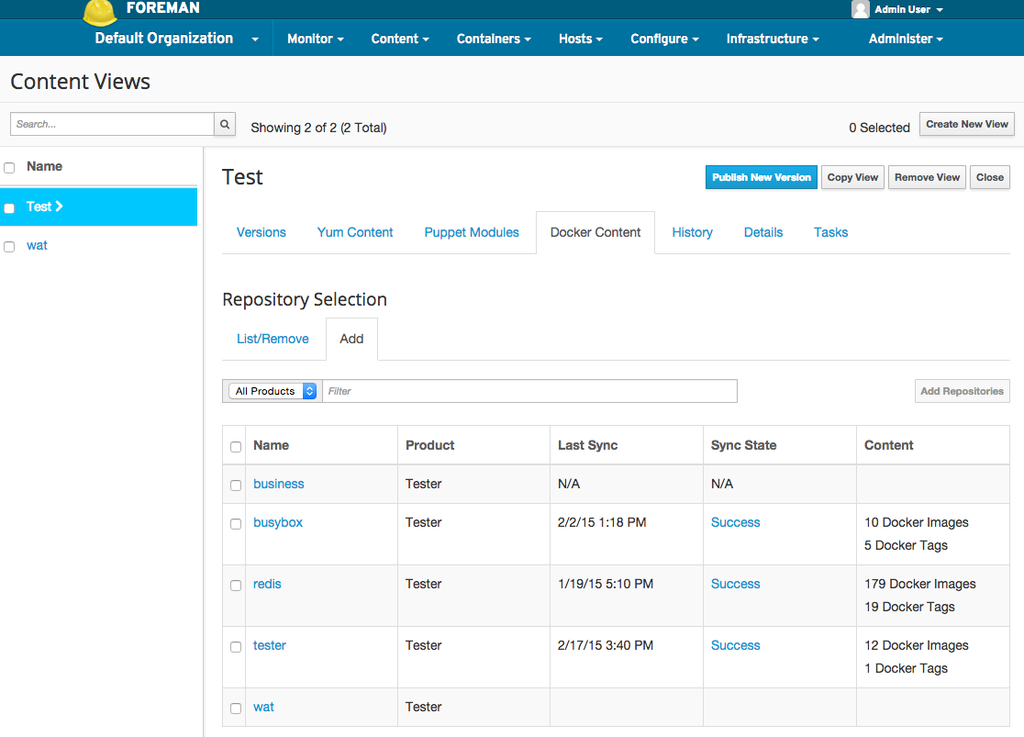
After creating a Content View, visit the Docker Content tab. Here you can select any Docker repositories you want to add to your Content View. After you’ve added Docker Repositories to your view, you may proceed as normal. Visit the Content View user guide for more information.
How to View and Pull Docker Content
To view Docker content contained with Katello, visit the Docker Tags page. This can be accessed under the Content menu at the top of any page.
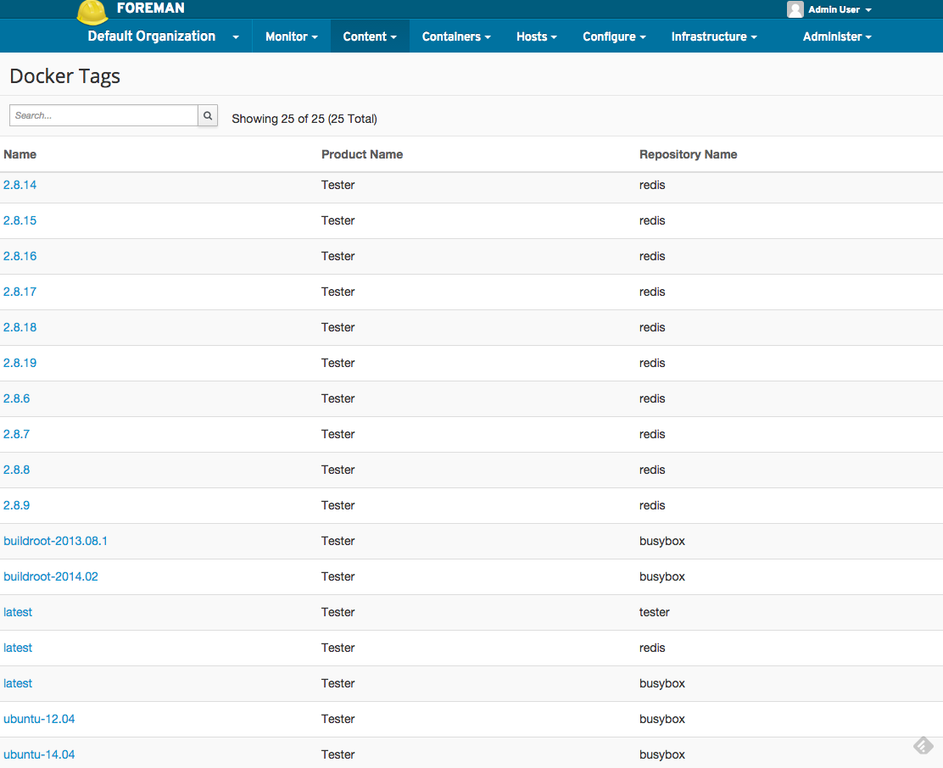
On the Docker Tags page, you can see a list of Docker Tags grouped by Repository in Katello. This shows you Tags grouped across Content Views and Lifecycle Environments. Suppose I wanted to pull the latest Tag from my redis repository, I would click the latest row for my redis repository.
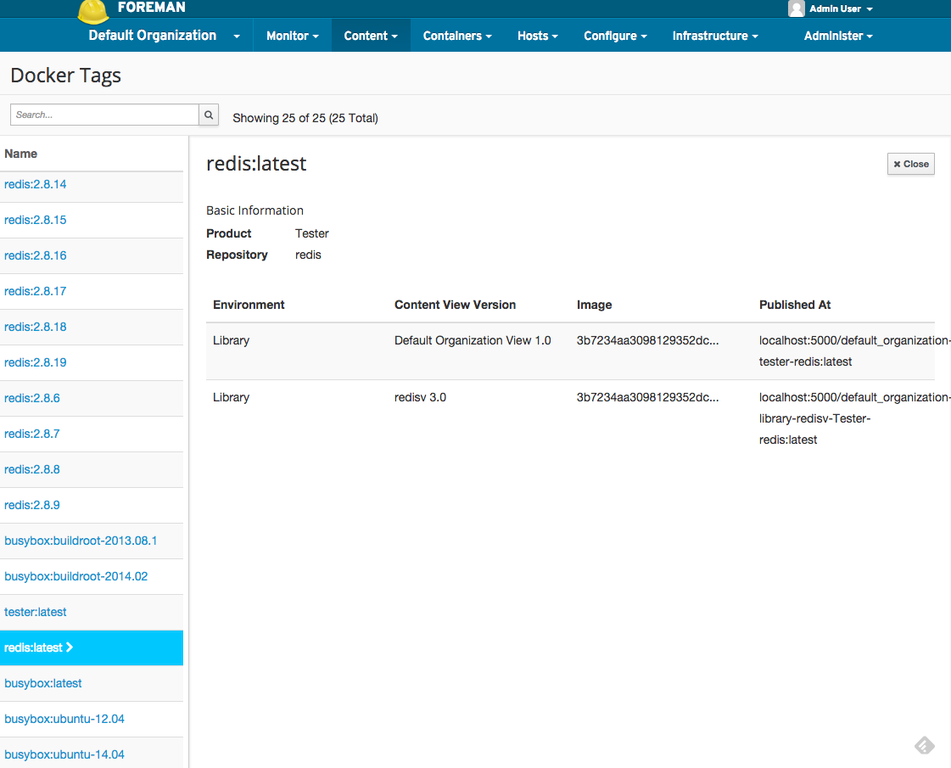
I can see here that my redis Repository has been added to a published Content View called redisv. If I want to use the tag from that Content View, I would just copy the Published At URL and then on my docker server I would run:
$ docker pull localhost:5000/default_organization-library-redisv-Tester-redis:latest
Pulling repository localhost:5000/default_organization-library-redisv-Tester-redis...
How to Provision Docker Content
See how to provision content in the documentation in the foreman-docker documentation. Provisioning content from Katello works in much the same way.
First, proceed to the new Container page by accessing it from the Containers menu at the top. Then, select the Local Content tab on the second step. This will allow you to select a Docker image from a published Katello repository which is in an environment/content view/Smart Proxy. Then just proceed in the wizard as per the Foreman Docker instructions. When you are finished, you should have a new container running from an image in Katello.